
Do you know the numbers behind your business? Having a deep understanding of how your store is doing will help you plan for the future and optimize your processes. As a result, you can identify what’s bringing in the most revenue and where you should be focusing your efforts.
KPIs are a crucial part in understanding your business. They help you see where your business is at right now and ensure you make data-backed decisions moving forward.
But which KPIs are the most important? There are many to choose from which can make it a difficult decision. Of course, it will partly depend on what kind of store you’re running and your overall goals, but here are some of the most important to get you started.
1. Average Order Value.
What is Average Order Value (AOV)?
AOV shows you how much, on average, customers spend on each order. That is, how much revenue you generate for each purchase regardless of how many items are in the customer’s cart.
How to Calculate Your AOV.
There’s a simple formula for calculating your AOV:
Total revenue / number of orders = AOV
For example, if you made $15,000 in revenue in a month through 350 orders, your AOV would be 15000 / 350 = $42.85.
How to Improve Your AOV.
Improving your AOV means increasing either the number of products a customer purchases in a single order or increasing product prices.
To do this, you might upsell or cross-sell products at checkout or bundle similar items together with a discount. Alternatively, you can implement a minimum order spend before free shipping is activated or provide product recommendations throughout the buying journey.
2. Conversion Rate.
What is Your Conversion Rate?
Conversion rates track the number of sales you’ve actually made against the number of visitors you’ve had to your site.
How to Calculate Your Conversion Rate.
Calculate your conversion rate by dividing the number of sales you’ve made over a specific time frame by the number of visitors you’ve had during the same time frame and multiply the result by 100.
Sales / site visitors x 100 = conversion rate
If you had 300 visitors in a month and made 75 sales the same month, your conversion rate would be 25%.
How to Improve Your Conversion Rate.
There are a number of tactics you can implement to improve your conversion rate.
Start by adding testimonials and reviews to your product pages to provide social proof and ensure the images you’re using are high-quality and show your products from every angle. On top of this, keep the checkout process as simple as possible and make sure you show the total price upfront to avoid any nasty surprises at checkout.
3. Gross Profit Margin.
What is Your Gross Profit Margin?
Gross Profit Margin (sometimes known as Gross Margin Ratio) tracks the financial health of your business. It essentially measures how much money is left over from sales after taking production costs into account.
How to Calculate Gross Profit Margin.
Calculating Gross Profit Margin involves subtracting the COGS from your total revenue over a certain time frame and dividing that number by the total revenue then multiplying it by 100.
(Total revenue – COGS) / total revenue x 100
If you made $5000 one month with your COGS at $1750, your Gross Profit Margin would be (5000 – 1750) / 5000 x 100 = 65%.
How to Improve Your Gross Profit Margin.
Improving your gross profit margin is a case of increasing your prices without increasing COGS. So, you might decide to try and increase sales volumes or optimize your COGS by researching more cost-effective manufacturers or bulk buying products.
4. Customer Lifetime Value.
What is Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)?
CLTV predicts how much revenue each customer will bring you over the years. Knowing this will help you determine your maximum acquisition costs and help you pinpoint who your most valuable customers are so you can attract more like them.
How to Calculate CLTV.
You can calculate your CLTV by multiplying the average value of each customer by their average lifespan.
Customer value x average customer lifespan = CLTV
If your average customer value is $50 and they stick around for an average of five years, your CLTV would be $250.
How to Improve Your CLTV.
Improving CLTV is a case of building deeper relationships with your customers so they keep coming back for more. The longer they remain a loyal customer with you, the higher their lifetime value becomes.
Make sure you consistently provide excellent customer service and always listen to and incorporate feedback from your best buyers.
5. Cart Abandonment Rate.
What is Cart Abandonment Rate?
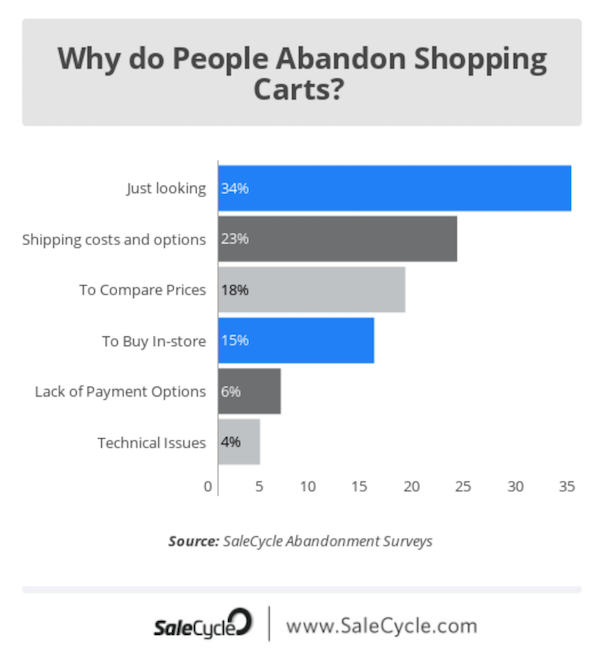
Cart abandonment rate lets you know how many people are adding items to their cart versus how many people are actually making it all the way through the checkout process.
It can help you determine why people aren’t purchasing. This might be because the shipping costs were too high for them, they want to compare prices, or they’ve decided to buy in-store instead.
How to Calculate Your Cart Abandonment Rate.
Work out your cart abandonment rate by dividing the number of shopping carts that have been created during a certain time frame by the number of completed purchases and multiply the result by 100. Then, flip the number round to get a percentage for how many people didn’t buy.
Shopping carts created / completed purchases x 100
Say you made 5,000 sales but 18,000 shopping carts were created. In this case, your cart abandonment rate would be 72.3%.
How to Improve Your Cart Abandonment Rate.
Improving your cart abandonment rate is a case of firstly, optimizing the checkout process, and then digging into why people put items into their cart without finalizing the purchase.
To get cart abandoners back, you can try running remarketing ad campaigns, reducing the number of form entries needed to buy (or, alternatively, adding a guest checkout option), and ensure your shipping costs and other additional fees are very clear upfront.
6. Return on Ad Spend.
What is Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)?
ROAS tracks the amount of revenue you make for each marketing dollar spent. It shows you how effective your ad campaigns or marketing methods are and helps you ensure you’re spending money on the right activities.
How to Calculate ROAS.
Calculating your ROAS involves dividing the total conversion value of each customer by your advertising costs.
Total conversion value / advertising costs = ROAS
If your total conversion value is $3500 and you’ve spent $750 on advertising, your ROAS would be 4.6 (or, you get $4.6 in return for every ad dollar spent).
How to Improve Your ROAS.
Improving your ROAS involves optimizing your ad campaigns and making sure you’re targeting the right people with the right keywords. Start by refining your keyword strategy, incorporating negative keywords, and optimizing product pages to encourage more conversions.
7. Average Order Size.
What is Average Order Size?
Unlike AOV, Average Order Size tracks the average amount of items each customer purchases in a single order.
How to Calculate Average Order Size.
Working out your Average Order Size is simple. Just divide the number of units sold in a certain time frame by the number of orders that were made during that same period.
Total units sold / number of purchases = Average Order Size
Say you sold 6,000 through 2,000 separate purchases one month. Your Average Order Size would be 3 – that is, customers buy 3 items per order on average.
How to Improve Your Average Order Size.
Improving your Average Order Size involves recommending relevant products to customers and exposing them to more potential items. To do this, you can bundle products together with a discount, cross-sell or upsell products at the checkout stage, or incorporate a minimum spending fee for shipping.
8. Cost of Goods Sold.
What is Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)?
COGS essentially tells you how much it costs you to produce the products your business sells. “Produce” here refers to manufacturing, material, and labor costs rather than distribution fees like shipping and advertising.
How to Calculate COGS,
Calculate your COGS by adding the cost of your starting inventory together with the total in purchases over the same time frame and subtracting the cost of your ending inventory.
Starting inventory + total purchases – ending inventory = COGS
If you had $10,000 of inventory at the start of the month, spent $6,000 on manufacturing, and ended up with $2,000 of inventory at the end of the month, your COGS would be $14,000.
How to Improve Your COGS.
Improving your COGS is a case of lowering manufacturing costs and optimizing the production process. This might mean you buy materials in bulk to get discounts, or it might mean you choose a cheaper manufacturer or increase your prices to cover the cost of creation.
KPIs Are the Key to Ecommerce Growth.
Knowing the numbers behind your business is crucial if you want to grow. KPIs like the ones we’ve mentioned here will give you a deeper insight into where your money is going and how much true revenue you’re bringing in. It’ll also give you a better understanding of your customers and what they want and need.
Tracking these KPIs should be a regular part of business. Urtasker recommends checking in with your numbers at least once a month to track any emerging trends straight away.
The post 8 KPIs You Need To Track For Ecommerce Growth appeared first on Young Upstarts.
from Young Upstarts https://ift.tt/2RQH6wX via website design phoenix

No comments:
Post a Comment